Know about Basic Concepts and Properties of Electric Charge
Know all about about the Electricity, its Charge, its Features, Unification of Electricity and Magnetism
All of us have the experience of seeing a spark when we take off our woolen/sweaters; we also experience a sensation of an electric shock either while opening the door of a car or holding the iron bar of a bus after sliding from our seat. The reason for these experiences is discharge of electric charges through our body, which were accumulated due to rubbing of insulating surfaces. You might have also heard that this is due to generation of static electricity.
ELECTRIC CHARGE
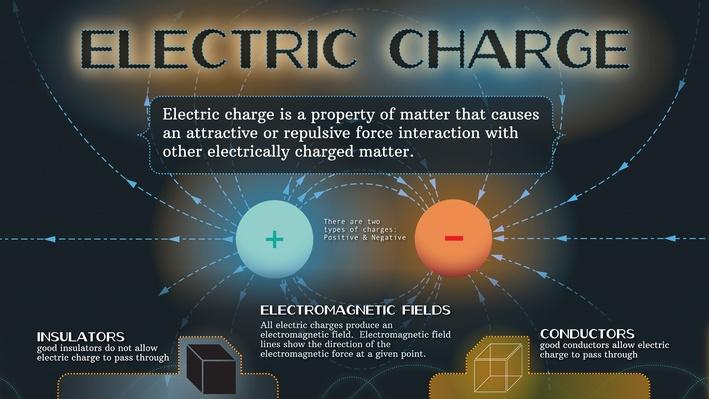
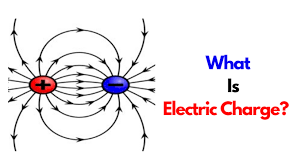
The name electricity is coined from the Greek word electron meaning amber. It was concluded, after many careful studies by different scientists, that there were only two kinds of an entity which is called the electric charge. There are two kinds of electrification and we find that (i) like charges repel and (ii) unlike charges attract each other.
The property which differentiates the two kinds of charges is called the polarity of charge.
Electric Charges and Fields neutralise or nullify each other’s effect. Therefore, the charges were named as positive and negative by the American scientist Benjamin Franklin. If an object possesses an electric charge, it is said to be electrified or charged. When it has no charge, it is said to be neutral.
UNIFICATION OF ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
In olden days, electricity and magnetism were treated as separate subjects. Electricity dealt with charges while magnetism described interactions of magnets, iron filings, compass needles, etc. In 1820 Danish scientist Oersted found that a compass needle is deflected by passing an electric current through a wire placed near the needle.
Read more: Important Revolutionary movement in India & their rise
Read more: What is the NIRVIK scheme? Features & Benefits
Ampere and Faraday supported this observation by saying that electric charges in motion produce magnetic fields and moving magnets generate electricity. The unification was achieved when the Scottish physicist Maxwell and the Dutch physicist Lorentz put forward a theory where they showed the interdependence of these two subjects. This field is called electromagnetism. The science of electricity and magnetism is the foundation for the modern technological civilisation. Electric power, telecommunication, radio and television, and a wide variety of the practical appliances used in daily life are based on the principles of this science.
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS
A metal rod held in hand and rubbed with wool will not show any sign of being charged. However, if a metal rod with a wooden or plastic handle is rubbed without touching its metal part, it shows signs of charging. Some substances readily allow passage of electricity through them, others do not. Those which allow electricity to pass through them easily are called conductors. They have electric charges (electrons) that are comparatively free to move inside the material. Metals, human and animal bodies and earth are conductors. Most of the non-metals like glass, porcelain, plastic, nylon, wood offer high resistance to the passage of electricity through them. They are called insulators. When some charge is transferred to a conductor, it readily gets distributed over the entire surface of the conductor. In contrast, if some charge is put on an insulator, it stays at the same place. When we bring a charged body in contact with the earth, all the excess charge on the body disappears by causing a momentary current to pass to the ground through the connecting conductor. This process of sharing the charges with the earth is called grounding or earthing. Earthing provides a safety measure for electrical circuits and appliances.
BASIC PROPERTIES OF ELECTRIC CHARGE
We have seen that there are two types of charges, namely positive and negative and their effects tend to cancel each other. Here, we shall now describe some other properties of the electric charge. If the sizes of charged bodies are very small as compared to the distances between them, we treat them as point charges. All the charge content of the body is assumed to be concentrated at one point in space.
BASIC UNIT OF CHARGE
This basic unit of charge is the charge that an electron or proton carries. By convention, the charge on an electron is taken to be negative; therefore, charge on an electron is written as –e and that on a proton as +e. The fact that electric charge is always an integral multiple of e is termed as quantisation of charge.
In the International System (SI) of Units, a unit of charge is called a coulomb and is denoted by the symbol C. A coulomb is defined in terms the unit of the electric current which you are going to learn in a subsequent chapter.
For more such informative articles stay tuned to OWN GURU.
