Reproduction in Human Beings- Understanding the Concept of Reproduction
Understanding Reproduction in Human Beings : Important Notes
Reproduction can be simply understood as the multiplication of an organism. Reproduction of an organism to produce and propagate offspring of the same kind is the universal characteristic of all living beings. There are two methods of reproduction-
- Asexual Reproduction– gives rise to an offspring that is genetically identical to its single parent
- Sexual Reproduction– involves creation of a new individual through the union of special sex cells called Gametes. The gametes are produced by the process of cell division called meiosis.
Read more: THE MAURYAN EMPIRE (324-185 BC)
Read more: GREEN WALL OF INDIA, VERTICAL GARDEN, INSIGHTS
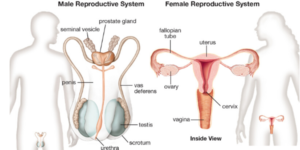
The Male Reproductive System–
It consists of two testes, each of which has mainly two functional components 1) seminiferous tubules 2) interstitial cells or Leydig cells. Its suspended in the pouch of scrotum. The scrotum has a paired duct system each consisting of epididymis, vasa deferens, ejaculatory duct and male urethra, sex organs including a prostrate, two seminal vesicles, two Cowper’s glands and a penis. Testes produce sperms and secrets testosterone. Prostrate, seminal vesicles and Cowper’s gland secrete fluids which mix with sperm to form semen. The duct system conducts the semen to the exterior.
The Female Reproductive System-
It consists of two ovaries and a duct system of two fallopian tubes and uterus and a vagina. Ovaries produce ova and secrete estrogens and progesterone. The fallopian tubes conduct the ovum towards the uterus, the uterus lodges the growing fetus and opens to the exterior through the vagina.
Gametogenesis is the formation of gametes for sexual reproduction. It is carried out in the gonads. The gametogenesis in male gonad is called Spermatogenesis. It is the production of sperms in the testes. The gametogenesis in female gonad is called oogenesis. It is basically the formation of ova in the ovary.
Spermiogenesis or transformation of spermatogonia into spermatozoa occurs in seminiferous tubules in 4 stages- Proliferation Phase, Growth Phase, Maturation Phase and Transformation Phase.
Oogenesis is the transformation of oogonia into ova. It takes place in the Graafian follicle of ovaries and is completed in 3 stages- Proliferation Phase, Growth Phase and Maturation Phase
Menstural Cycle-
The reproductive cycle of human females and other higher primates differs from non-primates in two ways. Firstly, the receptivity of the female is more ore less continuous. Secondly, there is bleeding or menstruation phase which is not met within the non-primates. Menstrual cycle occurs only when the released ovum is not fertilized. The lack of menstruation is indication of pregnancy but sometimes it may be caused due to complexities. In human females the duration of menstrual cycle is about 28 days with inner variations. This cycle is divided four phases-
- Menstrual Phase- it lasts for 3-5 days during which blood is discharged out. The bleeding is caused by the rapid regression of the uterine lining, rupturing of its blood vessels and sloughing away of portions of endometrium.
- Proliferative Phase- during this phase the uterine endometrium regenerates and becomes thickened- under the influence of hormone, Estrogen. This process lasts for about 10 days and extends from 6th to 14th day of cycle.
- Ovulatory Phase- this normally occurs on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle and lasts for only 6 hours. During this phase an ovum is released from the Graafian follicle to make its entry into the fallopian tube.
- Luteal Phase- after ovulation the Graafian follicle is transformed into corpus luteum which secrets the hormone progesterone. As a result, the uterine glands get active and endometrium becomes thicker for implantation of the fertilized ovum. In the absence of fertilization, the menstrual cycle begins afresh.
The menstrual cycle ceases at the age of 50 years and is termed as Menopause.
Fertilization and Embryo Development
During the sexual reproduction the sperms are discharged into vagina. Each discharge of semen contains millions of sperms. However only one of them fuses with ovum to fertilize it. The sperms deposited in the vagina swim up to the uterus and further up through the fallopian tubes where if a sperm meets an ovum it fuses with it resulting into the formation of a zygote. The zygote moves down the oviduct reaches the uterus and gets embedded in the endometrium on the 24th day of the menstrual cycle. The zygote divides repeatedly to form an embryo. The implanted embryo develops two membranes- Chorion and Amnion. The maternal and the embryonic tissues that come into intimate contact thus establish an important organ called the placenta, which exchanges material between the maternal and embryonic blood. With the growth of embryo, the placenta also grows.
The process of delivery of fetus is called parturition.
For more such informative articles stay tuned to OWN TV.
