A Brief Introduction of ASEAN-India Relations
What is ASEAN?
Globally, there was a lot of tension among various countries. In order to solve the issues among the neighbouring countries, several regional organizations were formed in the world. ASEAN is one of such regional organizations having a couple of countries as its members and who have signed a common agreement for peaceful trade practices.
What is ASEAN?
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional organization which was established to promote political and social stability amid rising tensions among the Asia-Pacific’s post-colonial states.
- The motto of ASEAN is “One Vision, One Identity, One Community”.
- 8th August is observed as ASEAN Day.
- ASEAN Secretariat – Indonesia, Jakarta.
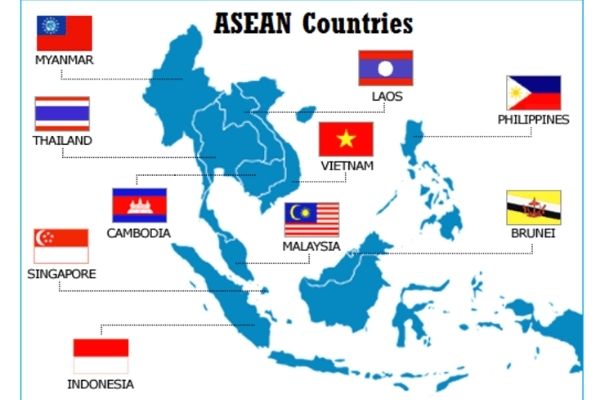
Member Countries of ASEAN
Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar and Cambodia.
Read more: Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) Initiative
Aim and Objectives
- To accelerate economic growth, social progress and cultural development for a prosperous and peaceful community of Southeast Asian Nations.
- To promote regional peace and stability through abiding respect for justice and the rule of law and adherence to the principles of the United Nations Charter.
- To promote active collaboration and mutual assistance on matters of common interest in the economic, social, cultural, technical, scientific and administrative fields.
- To collaborate more effectively for the greater utilisation of agriculture and industries, the expansion of their trade, the improvement of transportation and communications facilities and the raising of the living standards of peoples.
- To promote Southeast Asian studies.
- To maintain close and beneficial cooperation with existing international and regional organisations.
Strengths & Opportunities of ASEAN
- ASEAN commands far greater influence on Asia-Pacific trade, political, and security issues than its members could achieve individually.
- Demographic dividend – It constitutes the 3rd largest population in the world, of which more than half is below thirty years of age.
- Economic:
- 3rd largest market in the world – larger than EU and North American markets.
- 6th largest economy in the world, 3rd in Asia.
- Free-trade agreements (FTAs) with China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia and New Zealand.
- Fourth most popular investment destination globally.
- ASEAN’s share of global exports has also risen, from only 2 per cent in 1967 to 7 per cent by 2016, indicating the rising importance of trade to ASEAN’s economic prospects.
- The ASEAN Single Aviation Market and Open Skies policies have increased its transport and connectivity potential.
- ASEAN has contributed to regional stability by building much-needed norms and fostering a neutral environment to address shared challenges.
India and ASEAN
- India’s relationship with ASEAN is a key pillar of her foreign policy and the foundation of Act East Policy.
- India has a separate Mission to ASEAN and the EAS in Jakarta.
- India and ASEAN already have 25 years of Dialogue Partnership, 15 years of Summit Level interaction and 5 years of Strategic Partnership with ASEAN.
- Economic Cooperation:
- ASEAN is India’s fourth-largest trading partner.
- India’s trade with ASEAN stands at approx. 10.6% of India’s overall trade.
- India’s export to ASEAN stands at 11.28% of our total exports. The ASEAN-India Free Trade Area has been completed.
- ASEAN India-Business Council (AIBC) was set up in 2003 to bring key private sector players from India and the ASEAN countries on a single platform.
- Socio-Cultural Cooperation: Programmes to boost People-to-People Interaction with ASEAN, such as inviting ASEAN students to India, Special Training Course for ASEAN diplomats, Exchange of Parliamentarians, etc.
- Funds: Financial assistance has been provided to ASEAN countries from the following Funds:
- ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund
- ASEAN-India S&T Development Fund
- ASEAN-India Green Fund
- Delhi Declaration: To identify Cooperation in the Maritime Domain as the key area of cooperation under the ASEAN-India strategic partnership.
- Delhi Dialogue: Annual Track 1.5 event for discussing politico-security and economic issues between ASEAN and India.
- ASEAN-India Centre (AIC): To undertake policy research, advocacy and networking activities with organizations and think-tanks in India and ASEAN.
- Political-Security Cooperation: India places ASEAN at the centre of its Indo-Pacific vision of Security and Growth for All in the Region.
Check our Instagram : Ownguru
Facebook : Ownguru
If you have an interesting write-up or any suggestion, write to us at ownguru@gmail.com
Facebook Comments
